Radical prostatectomy is a surgical method used in the treatment of prostate cancer. This surgery involves removing the entire prostate gland along with the surrounding tissues.
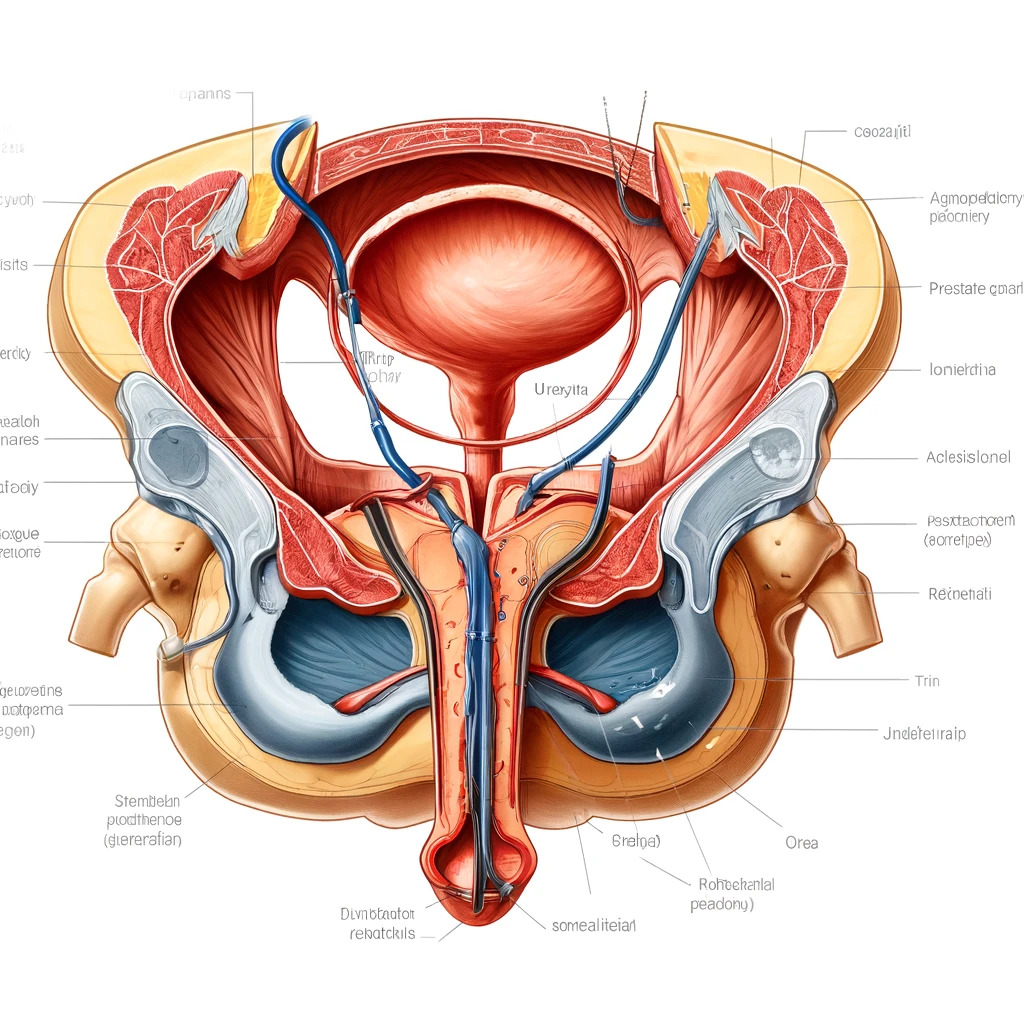
The goal of radical prostatectomy is to prevent the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. Radical prostatectomy is usually the preferred method when the cancer is limited to the prostate gland only.
Radical prostatectomy surgery can be performed using several different techniques:
When deciding how to perform the surgery, the patient's general health condition, the stage of prostate cancer and his preferences are taken into consideration. Each surgical method has its own advantages and risks. Therefore, it is important for patients to talk in detail with their doctors about their surgical options and expectations. Radical prostatectomy is usually one of the most effective treatments when prostate cancer is in its early stage and the cancer has not spread beyond the prostate.
Radical prostatectomy surgery is a complex surgical procedure that involves removing the prostate gland and some surrounding tissues. This surgery is used to treat prostate cancer and is usually recommended when the cancer is confined within the prostate. The procedure can be performed by different methods, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery or robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery. Here's an overview of how these methods are done:
Stage 1: The patient is put under general anesthesia.
Stage 2: The surgeon makes a large incision in the patient's lower abdomen. This incision is made either just above the pubic bone (retropubic approach) or behind the scrotum (perineal approach).
Stage 3: The surgeon carefully removes the prostate gland and, if necessary, surrounding lymph nodes. Meanwhile, it tries to maintain the connection between the urinary bladder and the urethra (the channel through which urine is excreted from the body).
Stage 4: The surgeon reattaches the cut parts of the bladder and urethra.
Stage 5: The incision is stitched and the healing process begins.
Stage 1: The patient is put under general anesthesia.
Stage 2: The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdominal area and inserts special instruments and a camera (laparoscope) through these incisions.
Stage 3: The camera and instruments allow the surgeon to view the prostate and its surroundings in detail on a large screen.
Stage 4: Using laparoscopic instruments, the surgeon removes the prostate and, if necessary, surrounding lymph nodes.
Stage 5: The urinary bladder and urethra are rejoined.
Stage 6: The incisions are stitched and the healing process begins.
Stage 1: The patient is put under general anesthesia.
Stage 2: The surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdominal area.
Stage 3: The instruments and camera of the robotic surgery system are inserted through these incisions.
Stage 4: The surgeon manipulates the instruments and camera using the surgical robot's control panel. This method provides the surgeon with a high degree of precision and flexibility.
Stage 5: Using robotic tools, the prostate and, if necessary, the surrounding lymph nodes are removed.
Stage 6: The urinary bladder and urethra are reconnected.
Stage 7: The incisions are stitched and the healing process begins.
All three methods have their own advantages and risks. The method chosen depends on factors such as the patient's health condition, the stage of the cancer, and the surgeon's experience.
Penuma Implant, Penuma Implant Before and After, Penuma Implant Cost, Penuma Implant Turkey detailed information for all about questions.
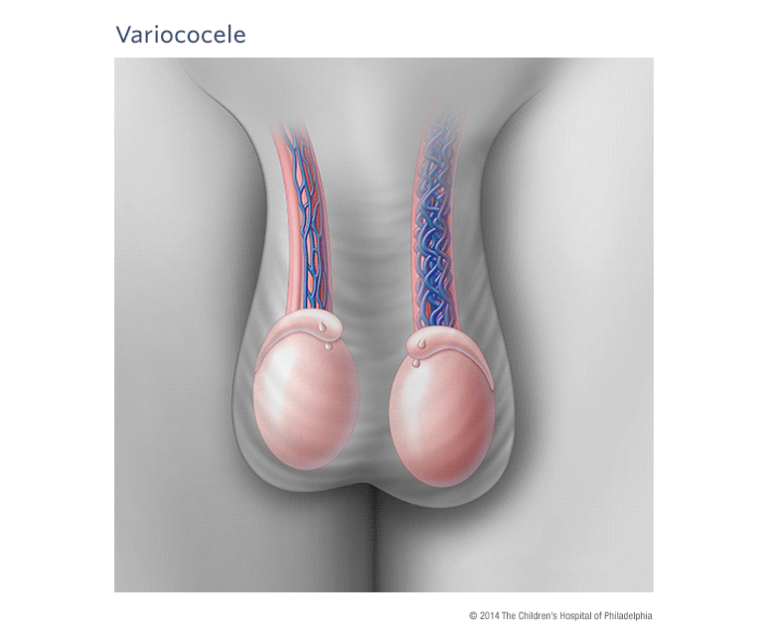
Varicocele, Varicocele Surgery, Varicocele Surgery in Turkey, Varicocele Surgery Cost in Turkey about detailed information

Detailed information about Penis Filler, Penis Filler Before and After, Penis Filler Turkey