
Bladder cancer is a cancer that is very common in our country and affects both men and women. Smoking has a very important place among the causes.
Numerous surgeries performed successfully
Hundreds of cancer patients regained their health
Hundreds of patients regained their health as a result of bladder cancer surgery
Numerous national and international publications in reputable medical journals
There are many reasons for bleeding in the urine. Bladder or kidney stones, bladder or urinary tract infections, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate, bladder or kidney cancer can cause bleeding in the urine.
The degree of bleeding and the presence of clots in the urine indicate that the disease may be more serious. For example, the risk is different only in cases of pink colored urine and clotted blood coming from the urinary tract. While it is necessary to seek a urologist's opinion even in cases of mild redness in the urine, in case of clotted bleeding, a urologist's opinion should be sought as soon as possible.
In case of bleeding in the urine, it is necessary to seek the opinion of a urologist as soon as possible.
Cystoscopy is the process of entering the urethra (urinary canal) and bladder with the help of a camera and imaging the inside. Masses that escape imaging methods such as ultrasound, tomography or MRI can be seen with the help of cystoscopy. While flexible cystoscopy, which is a softer device, can be performed locally under office conditions, cystoscopy can also be performed in the operating room under general anesthesia.
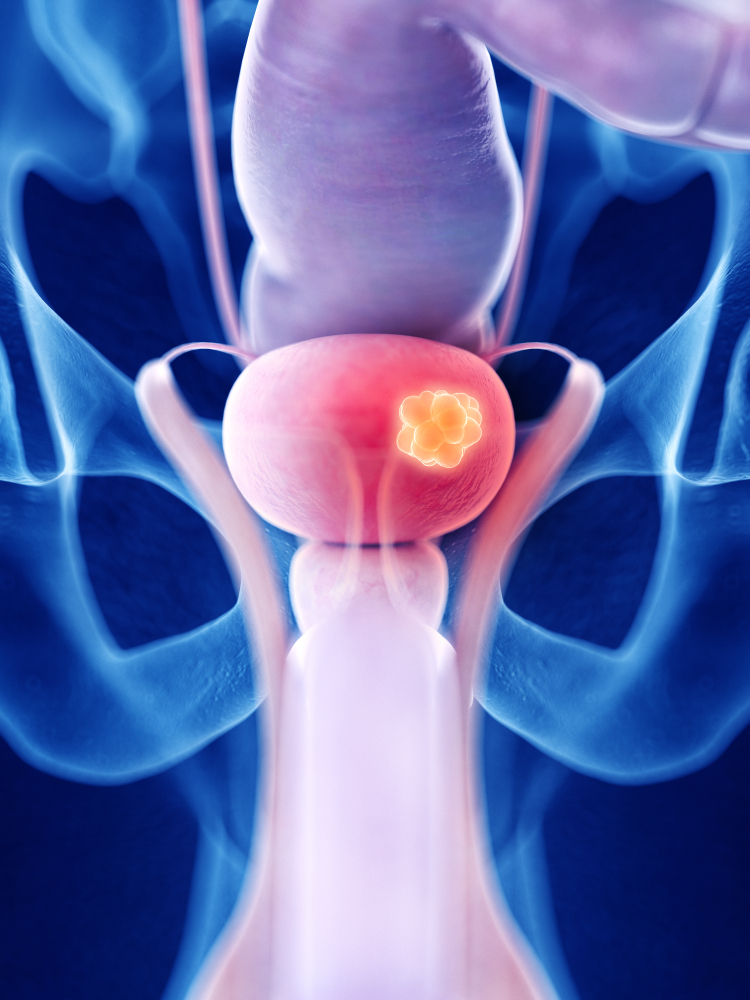
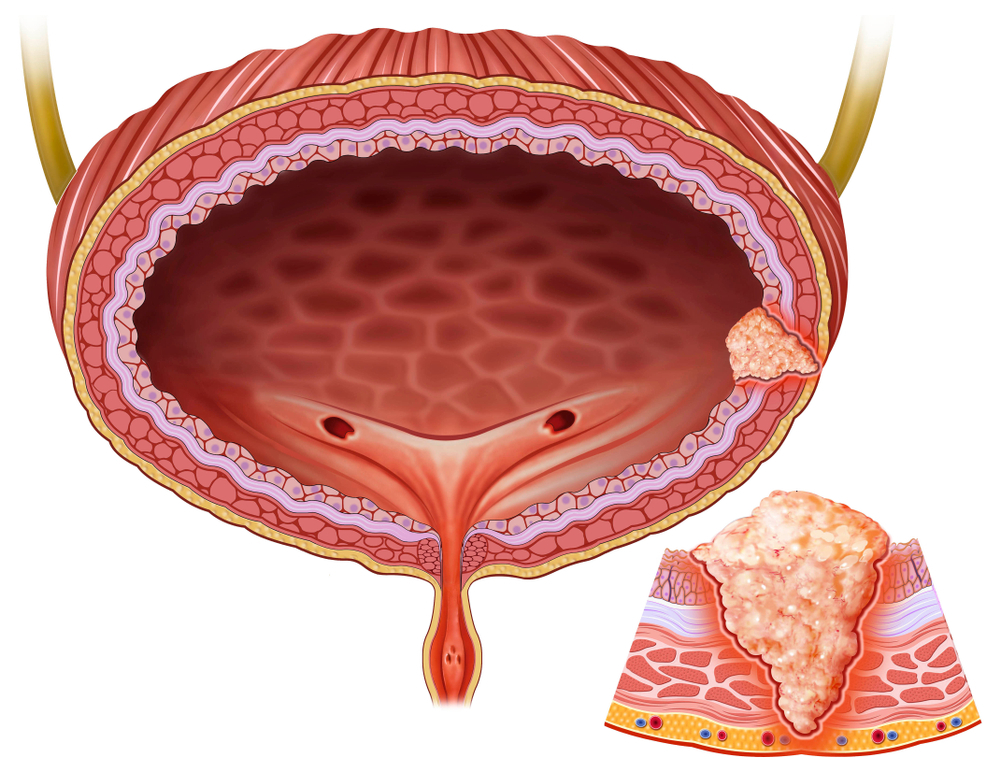
Masses seen in the bladder are called bladder tumors. The majority of masses seen in the bladder are malignant, but these masses can be removed with TUR surgery.
TUR surgery for bladder tumor is a surgery performed by entering the urinary tract using a closed method. The bladder is entered with a camera, and the tumor tissue seen in the bladder is cleaned. With this method, diagnosis can be made and treatment can be performed by removing the tumor at the same time.
It can be said that the bladder consists of roughly two layers. The inner two layers can be called superficial, and the outer two layers can be called deep layers. The epithelial layer lining the inside of the bladder and the supporting connective tissue just below it constitute the superficial tissues of the bladder. Cancers in these layers are called superficial bladder tumors. At the time of diagnosis, 75-80% of all bladder tumors are superficial bladder tumors.
Deep bladder cancer is a cancer that involves the muscle layer and deeper layers of the bladder, and since it reaches these layers, it has access to blood vessels. Since there is a possibility of the tumor spreading (metastasis) due to the blood vessels in these layers, more precise and comprehensive treatments are required.
Bladder tumor can spread. However, since there are no blood vessels in the superficial tissues, the possibility of spread is very low. Deep tissues are rich in vessels and are more likely to spread.
In superficial cases of bladder tumors, chemotherapy or radiotherapy is not applied. However, in deep tumors, chemotherapy can be applied before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant). In cases where surgery is not suitable for deep bladder tumors, radiotherapy may also be considered.
BCG treatment is a treatment applied to superficial bladder tumors. Approximately 4-6 weeks after the surgery, it is planned to destroy the bladder tumor by the body by injecting attenuated BCG vaccine into the bladder by catheter. This type of treatment is called immunotherapy.
In superficial bladder tumors, if the tumor is very large; In BCG failure; In deep bladder tumors, bladder removal may be necessary. The reason for removing the bladder is to intervene before the tumor spreads, thus keeping the patient alive. It is possible to say that when bladder cancer spreads, the patient faces vital problems.