
Pediatric urology is a branch of medicine that deals with congenital or acquired diseases of the urinary and genital systems of childhood children. Diseases treated in this area generally involve organs such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and in boys, the testicles and penis. Pediatric urology deals with urological problems in both boys and girls and is a subspecialty of pediatric surgery.
Some common diseases in the field of pediatric urology are:
Hydronephrosis: It is a condition that causes the kidneys to swell as a result of accumulation of urine in the kidneys. This can occur due to obstruction at any level of the urinary tract or reflux such as vesicoureteral reflux.
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR): It is a condition in which urine leaks back from the bladder to the ureters and sometimes to the kidneys. This can lead to infections and cause kidney damage.
Ureteropelvic Junction Stenosis (UPJ Stenosis): It is a condition where there is a narrowing in the area connecting the kidney to the ureter. This condition can obstruct urine flow and cause hydronephrosis.
Hypospadias: It is a condition in which the opening of the urethra on the lower surface of the penis in boys is congenitally in an abnormal position. Treatment is usually done by surgical methods.
Undescended Testis (Cryptorchidism): It is the condition in which one or both testicles do not descend into the scrotum (bag). If not treated early, the risk of infertility and testicular cancer may increase.
Nocturnal Enuresis: Involuntary urinary leakage while sleeping at night. This condition usually develops without an underlying urological problem, but may sometimes require a urological evaluation.
Neurogenic Bladder: Impairment of bladder functions due to nervous system diseases. This condition can affect the way you urinate and lead to urinary tract infections.
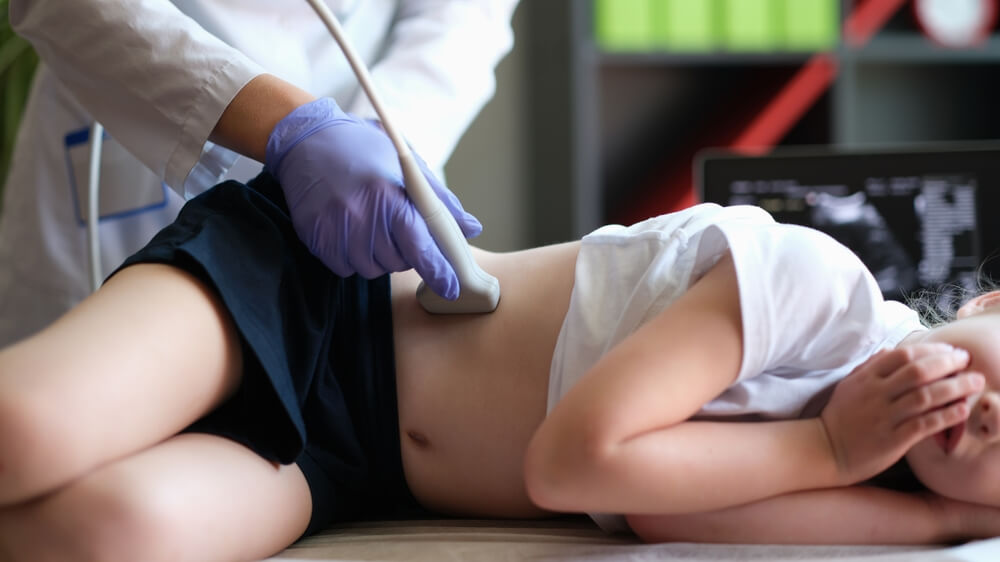
For the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to pediatric urology, imaging methods such as ultrasound, MRI (Magnetic Resonance), VCUG (Vesicoureteral reflux radiography) and in some cases surgical interventions are generally used. Because the urological health of children differs from that of adults, it is important that they be evaluated and treated by pediatric urologists who specialize in this field.